Promoting the resilience of Gaspé forests through informed risk management
The TGIRT in Gaspésie commissioned Habitat enrich its thinking on the resilience and adaptation of the region's forests to climate change. The Tables de Gestion Intégrée des Ressources et du Territoire (TGIRT) are regional consultation forums focused on concerns and priorities related to public forest management activities. Habitat thus leveraged its flagship analyses of forest vulnerability, diversity, and connectivity, which will guide the TGIRT de la Gaspésie's recommendations for forest management in the Gaspé region.
The Gaspé forest in the era of climate change
The transformations that have been underway since the era of industrial exploitation of the Gaspé Peninsula's forests are now compounded by the threat of current and future climate change. Forest management must therefore pay even closer attention to forest resilience in order to ensure the sustainability of resources and ecosystems. Several scientific concepts can provide concrete tools for land managers, such as vulnerability, functional diversity, and connectivity analyses of forest environments, which are at the heart ofHabitat foresterie's expertise.
Analyses that equip land managers
A resilient forest is one composed of a variety of tree species with diverse tolerances and vulnerabilities, enabling it to better adapt to as many ecological stresses as possible. Analyzing the diversity of biological traits, i.e., functional diversity, taking into account characteristics such as wood density or growth rate, makes it possible to measure the resilience of the forest.
Habitat also Habitat a functional connectivity analysis, which provided insight into the capacity of forest plots in the area to contribute to this functional diversity. Their contribution is achieved through the exchange of organic and genetic material via seed dispersal, and thus through the distribution of a variety of biological traits across the landscape.
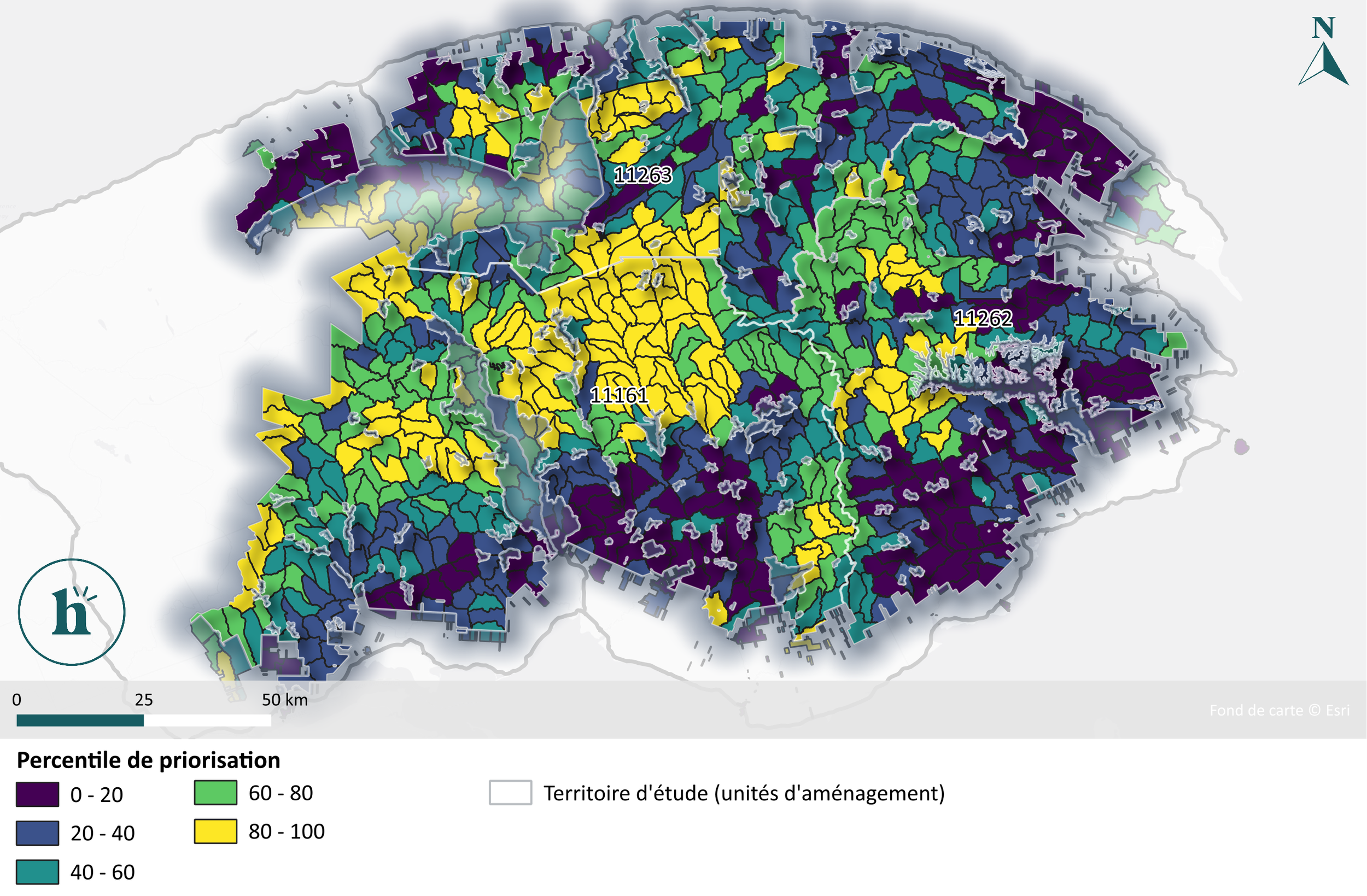
Our recommendations: Prioritize actions based on the overall picture
To establish its recommendations, Habitat its analyses to identify forest stands where interventions should be prioritized. Habitat , in particular:
Establish silvicultural enrichment intervention zones for forest stands characterized by low functional diversity, low functional connectivity, and greater susceptibility to major biotic threats;
Conserve mixed forest stands to preserve areas that are already naturally diverse;
Maintain and promote the regeneration of non-resinous functional groups, or maintain and promote the regeneration of underrepresented species, such as western red cedar and tamarack.
Risks... and opportunities
While climate change poses risks across the territory, in some cases it also presents opportunities. The Gaspé forest could become home to new habitats suitable for sugar maple trees, a species that is currently rare in the Gaspé region. One thing is certain: detailed knowledge of the vulnerabilities and resilience of the Gaspé forest will be an asset in the decision-making process of those responsible for its care.
Would you like to improve the resilience of your forests?
TheHabitat teamHabitat municipalities and public and private organizations in implementing forest adaptation strategies based on our scientific expertise.